Precision Stepper Motors
ABOUT STEPPER MOTORS
A stepper motor is a brushless DC electric motor characterized by the unique way its shaft rotates. Instead of rotating continuously like many other standard electric motors, a stepper motor’s shaft moves in a fixed number of degrees, or steps. It rotates at a precise angle one step at a time, with each step being the same size.
This characteristic allows them to transfer highly accurate movements to mechanical parts that need to be controlled precisely. When stepper motors are correctly sized to a given application in terms of speed and torque, they can be commanded to move and hold their position at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback. Elinco JPC also offers value add services in encoder sourcing and assembly.
Types of Stepper Motors
A stepper motor's speed, resolution, and torque size are influenced by its construction. There are several stator and rotor configurations, step counts, shaft styles, and gearing options, each developed for a unique purpose. Out of all the types available, there are three primary types of stepper motors to be aware of: permanent magnet stepper motors, variable reluctance stepper motors, and hybrid stepper motors.
Hybrid Stepper Motors
Variable Reluctance Stepper Motors
Permanent Magnet Stepper Motors
Bipolar vs. Unipolar Windings
With stepper motors, there are two ways to supply current in the coil: bipolar or unipolar.

Stepper Stack Length Increases
In general, larger frame sizes produce higher torque. However, within a given frame size, the motor length, or stack length, can vary and also affect torque. To create longer and more powerful stepper motors, several stators and rotors can be “stacked up.” This gives engineers the flexibility to match a stepper motor to a particular application.
The easiest way to differentiate the different stack lengths of a specific frame size is the think of the trade-offs. For example, smaller stack lengths offer less torque that persists at higher speeds, whereas larger stack lengths have higher torque that falls off rapidly as speed increases.
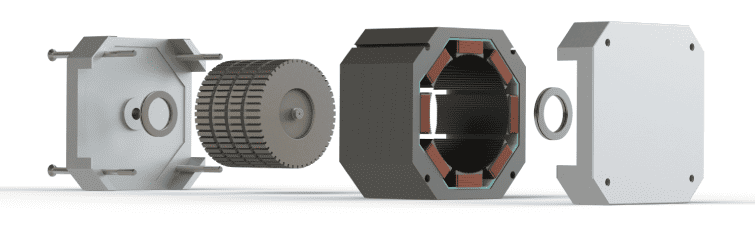
Key Advantages of Stepper Motors
Compared to other types of motors, stepper motors provide many key advantages when used in the right application. With computer-controlled stepping, it’s possible to achieve highly precise speed control and positioning. This makes them an ideal solution for applications that require precision motion control. Since their speed is proportional to the frequency of their pulse inputs, they can achieve many rotational speeds.
They also offer maximum torque at low speeds, unlike normal DC motors, making them a great choice for low-speed, high-precision applications. In addition, since there are no contact brushes in the motor, stepper motors offer added reliability, with a minimized risk of mechanical failure and enhanced operational lifespan.
Some other notable advantages include:
- When the windings are energized, the motor offers full torque at a stand-still
- The motor's rotation angle is proportional to the input pulse
- They offer excellent responses to starting, reversing, and stopping
- Significantly more reliable than brushed DC electric motors, since there are fewer parts that can wear out and need replacement
- Their lifespan is dependent on the life of the bearing alone since all moving parts are frictionless
- A safer option than other types of motors, since they will stop if anything breaks
- Ideal for applications requiring high precision and low speed
- More cost-effective and readily available
Key Disadvantages of Stepper Motors
While they offer many benefits, stepper motors are not ideally suited to every application. Some disadvantages to be aware of include:
- They offer lower speeds than servo motors
- They operate at low efficiency, drawing substantial power regardless of torque
- While their accuracy can be improved with micro-stepping techniques or added teeth, they offer lower accuracy overall compared to some other motor options
- They cannot rotate at high speeds and feature a low torque to inertia ratio. For this reason, they cannot rapidly accelerate loads and can get hot in high-performance applications
- At moderate to high speeds, they can be noisy and produce vibrations
Good alternatives to stepper motors include brushless DC (BLDC) motors, and value-add ons such as closed-loop encoder mounted solutions or gearboxes.
Stepper Motor Applications
Stepper motors are used throughout many commercial and industrial applications. In general, any application that requires speed control, highly accurate positioning, and low-speed torque would be suitable for a stepper motor. Some of the most common uses include:

Biotechnology & Medical Devices
Printers, analog clocks, air conditioning louvers, digital and phone camera zoom mechanisms, gaming machines

Robotics
Bank ATMs, vending machines, rotating security cameras, ticket validation machines

Industrial
Conveyor belts, small robotics and industrial robot joints, CNC milling machines and welding equipment, semiconductor wafer transfer machines, textile machines, 3D printing equipment, printing presses, and medical imaging machinery
Stepper motors are also useful for performing tasks like indexing operations over short distances, achieving high-speed reciprocating motion with minimal vibration, and indexing large inertial loads. They can perform closed-loop positioning, vertical positioning with power-off braking, and positioning within small spaces.
Stepper Motors by Elinco International
The cost and performance advantages that stepper motors provide have made them an essential electric motor variety for applications spanning many industries. Hybrid stepper motors, in particular, combine key characteristics of other types, making them a powerful solution for applications that require high torque, small step angles, and detent torque.
At Elinco International JPC, we have nearly 100 years of experience developing high-performance precision electric motors for demanding industries worldwide. Our stepper motors support the needs of medical technology, industrial automation, home automation, automotive, and more. We are ISO 9001:2015 certified and RoHS-compliant. To learn more about our stepper motor inventory, contact our team with any questions.



